


Using the proper blood pressure measurement instrument is necessary, especially for people who are at risk of having abnormal blood pressure levels. The blood pressure reflects the force which drives blood along the blood vessels in the circulatory system. To monitor the blood pressure, it is important to use aproperly calibratede quipment which can detect abnormalities that may lead to potential complications.
To measure your blood pressure manually, you will need a sphygmomanometer and a stethoscope.
This instrument is often called by laymen as the "blood pressure (BP) cuff." You will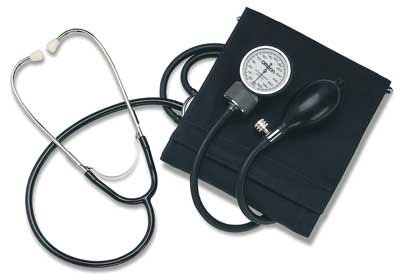 find different types of BP cuffs in use. One type is attached to the wall (usually near a patient's bed in the hospital), but most BP cuffs are portable. These devices basically work the same way, and have the same parts—the bladder, which is connected by a tube to the bulb that has a release valve, and a pressure gauge, which is either ananeroid or mercury type.
find different types of BP cuffs in use. One type is attached to the wall (usually near a patient's bed in the hospital), but most BP cuffs are portable. These devices basically work the same way, and have the same parts—the bladder, which is connected by a tube to the bulb that has a release valve, and a pressure gauge, which is either ananeroid or mercury type.
This is a listening device that aids in the measurement of blood pressure. Its parts include:
Here is a video to help you understand how to measure blood pressure with the manual blood pressure monitors:
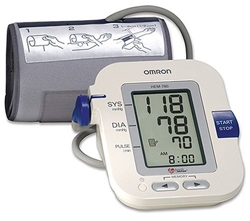
Automatic monitors, also known as electronic or digital blood pressure monitors, are battery-operateddevices which use microphones to detect pulsations in the artery. Inflation of the cuff wrapped around the arm inflates and deflates automatically when the “start” button is pressed. This type of BP monitor may be found in pharmacies, supermarkets and shopping malls. When using automatic BP monitors, avoid those which measure blood pressure from the finger or wrist since they are not accurate.
Automated devices are currently available in four generic types:
This is a small device worn for 24 to 48 hours to take your blood pressure automatically throughout the day. This is used for people who have inconsistent BP readings. It gives a complete picture of blood pressure fluctuations. The cuff on the arm is attached to another device worn on the waist, which records readings regularly. Some models transmit the readings to medical personnel who monitor your blood pressure results almost in "real time."
These monitors make BP measurements repetitively at regular time intervals and often include other vital signs and alarms. Designed for bed-side BP monitoring in clinics and hospitals, they provide accuracy but are often expensive.
These devices make single measurements and may record other vital signs. They are popular for routine clinical use as well as general ward applications.
These devices make single BP measurements only and may be used for home monitoring as well as in clinical practice.