


Every year, there are approximately 150,000 Americans finding they have central nervous system disorder which may cause seizures. 1 in 26 people at some point of life will be diagnosed with it.Seizures can cause symptoms like temporary blank staring, uncontrollable twitching, or loss of awareness. Seizures should always be watched closely because sometimes minor seizures may be life-threatening if they occur during driving, swimming, diving and other activities.
The brain is filled with thousands of transmitters known as neurons. These nerve cells use electrical impulses and chemicals to communicate with each other and tell our muscles and organs what to do. If a person has epilepsy, sometimes these signals become crossed and the electrical current becomes scrambled. Instead of passing in an orderly manner from one cell to the next, the signals spill over into a clump of cells or even throughout the whole brain. That is when a seizure occurs. If only part of the brain is affected, the seizures are classified as focal seizures, also known as partial seizures.
The symptoms of focal seizures can vary widely depending on which part of the brain is involved.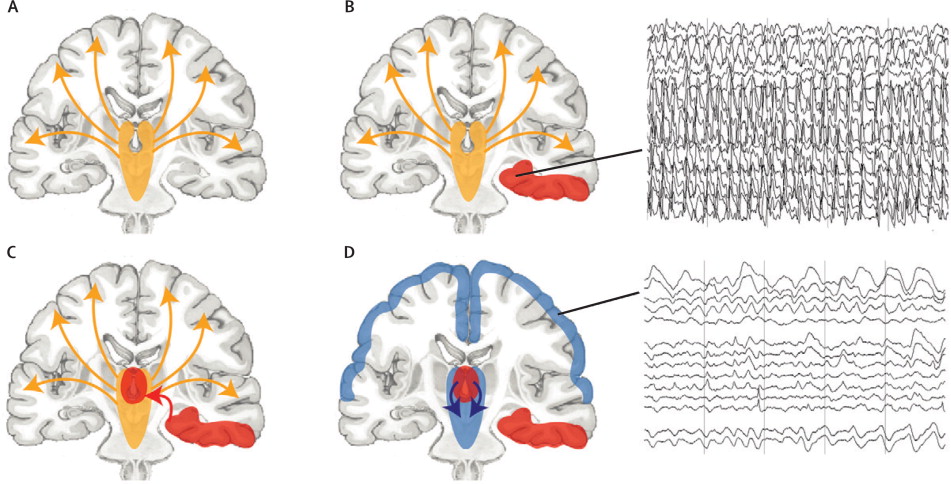 Although the seizures normally occur in the same part of the brain in an individual, they can appear completely different from one person to another so it becomes more difficult to diagnose the condition. Some of the symptoms that may occur include:
Although the seizures normally occur in the same part of the brain in an individual, they can appear completely different from one person to another so it becomes more difficult to diagnose the condition. Some of the symptoms that may occur include:
There are 3 types of partial seizures. Those include simple partial seizures, where one remains aware of their surroundings, complex partial seizures, where awareness is lost, and those partial complex seizures that grow into secondary general seizures, which begin as a simple, focal seizure but advances into a full-blown seizure where loss of consciousness and convulsions occur.
Simple Focal Seizure
There are 4 types of simple focal seizures, divided by the symptoms experienced and when the symptoms occur, the person does not lose awareness of his or her surroundings.
Complex Partial Seizures
On the other hand, complex partial seizuresinclude loss of awareness. The affected person may simply stare into space and not respond when spoken to or ignore other stimuli. They may show automatous symptoms such as lip smacking, arm jerking, head shaking, repeating of a word or phrase, or others. The movements, although coordinated, are usually repetitive and purposeless.
If you or someone you know is showing symptoms of focal seizures or other signs of epilepsy, a thorough evaluation by a physician is necessary. They will gather a complete medical history, run tests, such as anelectroencephalogram (EEG) to see the electrical flow in the brain or a brain scan to look for scar tissues or other abnormalities that may be causing the seizure.
If you witness a person having a seizure, there are certain steps you should take to prevent them from getting hurt. Those include:
Seizures normally last about 1 to 2 minutes. If a seizure continues for more than 5 minute, or if the person is a pregnant woman or a diabetic, it is considered a medical emergency and medical assistance should be sought immediately. Following a seizure the person may feel disoriented for several minutes.