


Medical shock differs from the psychological or emotional shock which occurs as a result of frightening or traumatic emotional incident.In medical terminology, shock results from insufficient flow of blood in the entire body. Most of the time, it comes along with severe illness or injury. If it doesn’t get controlled immediately, it may lead to emergency conditions like hypoxia, cardiac arrest or damage organ. If treatment isn’t initiated, then the symptoms may aggravate with time.
Shock may be caused by trauma, blood loss,heatstroke, severe infection, poisoning, allergic reactions,severe burnsand others.
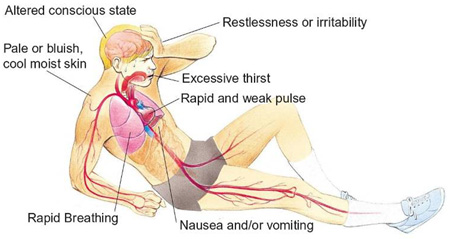
In a condition of shock, the body is deprived of sufficient oxygen or blood. Untreated condition will consequently result in a permanent damage of organ or worse, death. Given below are the sign and symptoms that are likely to appear:
Apart from the general sign and symptoms, every type of shock has its own particular signs and symptoms. Identify the type and choose the treatment based on the type and symptoms.
It results from an infection and is characterized by initiation of full body inflammation. Elder people and those who are with a comprised immune system are more susceptible. This inflammation leads to formation of tiny blood clots that prevent the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the vital body organs.The third stage of sepsis is the septic shock when the blood pressure declines notably. It may result in heart, respirator or organ failure, even death.
Sign and symptoms:
It is a potentially serious allergic response characterized by dilated blood vessels, deteriorating blood pressure, hives and swelling. This type results from the development of antibodies against an allergen. This antibody may produce an exaggerated reaction against even a harmless substance like food. Exposure to the substance may cause binding of antibodies to allergen, resulting in a huge amount of histamine, a protein which is responsible for the symptoms. Below are some allergic reactions that increase the risks: sting or insect bite, medicine allergies such as allergy to penicillin, food allergies like allergy to egg, peanut or milk, prior anaphylactic shock, and latex allergy.
Sign and symptoms:
Sever Symptoms:
Note: If a person shows sever symptoms as mentioned above, he/she should be sent to hospital in 30-60 minutes since the symptoms could be fatal.
This kind of shockhappens when the heart fails to pump, leading to minimized cardiac output followed by hypoxia and acute hypoperfusion of organs and tissues. It is characterized by sustained decline in blood pressure and hypoperfusion of tissues. It usually occurs due to acute myocardial infarction. Cardiogenic shock needs instant resuscitation.
Sign and symptoms:
Also called hemorrhagic shock, it is a potentially serious condition that occurs upon losing 20% of the body’s total blood or fluid supply. As a result, heart fails to pump enough blood to the body, leading to organ failure. For survival, this emergency condition must be treated immediately.
Sign and symptoms:
Symptoms of internal haemorrhage are:
It occurs due to the injury to central nervous system like the spinal cord and brain, causing disruption of the functions that take place in nervous system. This consequently influences the distribution of blood within the entire body.
Sign and symptoms:
Without even giving a second thought, the first thing you should do is to grab the phone and dial 911 or the emergency number in your locality. While waiting for the ambulance, you can try the following:
To know more about shock treatment, watch the following video: