


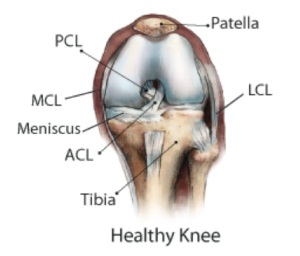
Injury to the lateral collateral ligament or LCL (the ligament along the outer side of your knee) can cause instability to your knee. Since the ligament connects the thigh bone to the small bone of your lower leg and ankle, LCL injury can cause symptoms like inflammation and lack of knee joint stability.
LCL injury can cause mild to severe symptoms, depending on the degree of damage involved. A mildly sprained ligament may not have any symptoms at all, but a partial or completely torn ligament may cause symptoms such as:
An LCL injury usually occurs when the lateral collateral ligament is torn after a direct blow is sustained inside of your knee. This force results in stretching of the ligament on the outside of your knee, causing a tear. This injury commonly occurs in sports that involve quick and repetitive stops and turns, such as basketball, skiing, soccer, or those where violent collisions are involved, such as hockey or football.
Most injuries in the knee involve the supporting ligaments, not only the joint itself. Injuries involving the collateral ligaments are often caused by forces that push the knees sideways, usually due to contact injuries. Repeated stress can also cause injury to the ligament due to loss of normal elasticity.
Upon consultation, your doctor will ask about your medical history andsymptoms. He will conduct a physical examination to check on your injured knee, comparing it to the other one. LCL injury may be easily diagnosed with thorough physical examination.
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may order other tests such as:
The diagnosis of LCL injury is completed by describing the extent of injury, which is classified into grades:
Sometimes it may be difficult to evaluate the extent of injury or damage to the ligament because of intense swelling and pain in the knee. Your doctor may apply ice, raise your knee and ask you to use a light splint. When your pain is reduced, he may examine you again to make a more accurate diagnosis.
Treatment options for an LCL injury may depend on the severity as well as your lifestyle. Treatments for minor LCL injury may include:
Treatment for severe injuries may also include surgery, physical therapy and rehabilitation. Surgery may involve ligament reconstruction or repair, especially when other ligaments or structures are involved.
LCL injury often occurs as a result of an accident and is therefore difficult to prevent. However, several measures could help reduce the risk of LCL injury, including: