


Your MCL or medial collateral ligament is a band that allows the knee to rotate, prevents it from bending inward, and keeps it stable. This wide ligament connects your femur to the tibia, running down the inner side of the knee. MCL injury can lead to swelling, pain and knee instability.
MCL injury is marked by symptoms just like those of other problems in the knee. Consult a doctor for proper evaluation and treatment if you experience these MCL injury symptoms:
MCL injuries often occur when the knee sustains a direct hit on the outer side. This causes stretching of the ligaments on the inner side of the knee, which can also tear them. Many athletes suffer from tears of both the MCL and anterior cruciate ligament. MCL injury can also occur through repeated stress, which causes it to lose its elasticity, just like a worn-out or old rubber band.
After a knee injury, a doctor will ask you how you got injured, your symptoms, and if you have experienced other injuries in the past. He may also ask you about your goals and athletic plans to help determine the best treatment options for you.
The physical examination involves checking the inside of your knee for pain and tenderness. Your doctor may also test the stability of your knee by applying pressure on the outer side of your knee while your leg is bent, and again while it is straight.
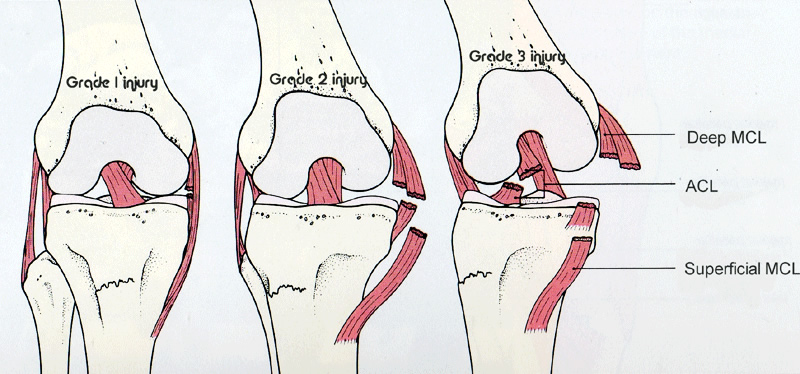
The intensity of pain and degree of looseness in your joint will determine the classification of your MCL injury as follows:
There are several treatment options for MCL injury, which may vary according to the extent of ligament damage. In most cases, the injury heals with rest.
The treatment for a knee injury should begin as soon as possible to reduce pain, swelling and stabilize the joint. Immediate treatment includes:
During recovery from your MCL injury, your aim is to improve the strength of the injured knee and to prevent more injury. Your treatment may include the following options:
An MCL injury rarely requires surgery. However, surgery may be needed when the injury involves other structures or the MCL is torn, and self-repair is not possible.
Before surgery, the surgeon may use an arthroscope to examine the severity of your knee injury. Arthroscopy is a procedure that includes inserting a pencil-thin instrument with a camera into a small skin incision into the knee point. However, unlike other knee surgeries, surgery on the MCL cannot be done arthroscopically. The reason is that the ligament is outside the joint.
Following arthroscopic examination, the surgeon will incise the skin and tissues behind the knee and reattach the torn ligament using stitches, staples or metal screws.